CHARON-AXP for Windows - Start service
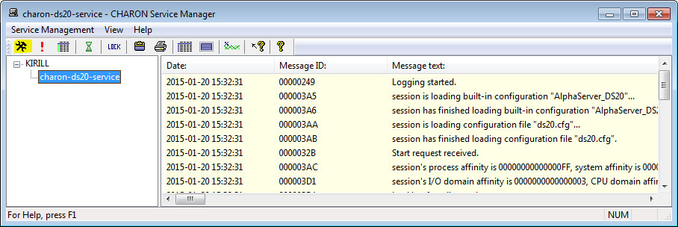
In the main window of the utility, select the target CHARON service ("charon-ds20-service" in our example) and press the "Service" button (labeled with yellow on the screenshot below):
The "Service Management dialog" will appear:
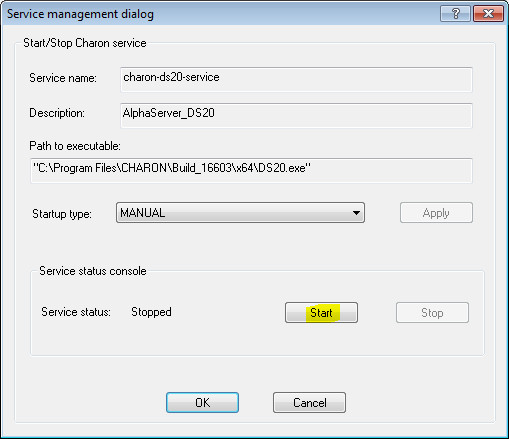
The "Service Management dialog" shows the current status of the selected CHARON service and permits changes to its start up type and to start and stop it. The example screenshot above shows that the service "charon-ds20-service" startup type is "MANUAL" (can be started / stopped only manually) and in the "Stopped" state - these are the default values.
Press the "Start" button to start the service:
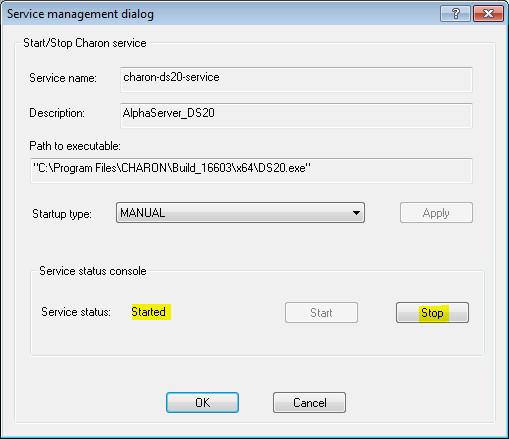
CHARON will start and the Service status will be "Started". To stop the service, press the "Stop" button.
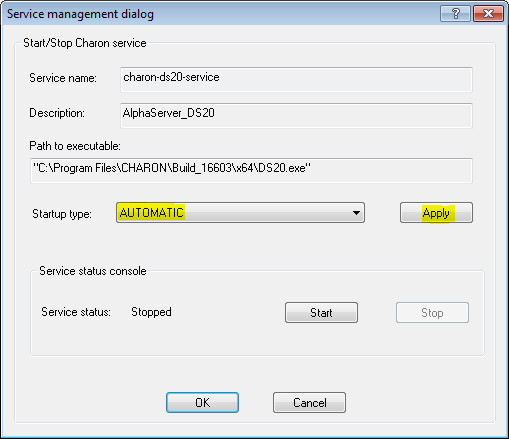
It is possible, and often desirable, to configure the selected CHARON service to start when host operating system starts. To enable this capability, select "AUTOMATIC" in the "Startup type" drop-down box and press the "Apply" button:
Note that a certain delay may occur before the Sentinel Run-time process finds the network license on CHARON-AXP host system startup. If the CHARON-AXP service is starting automatically on the host system, it may report a "License not found" error and exit.
This problem can be avoided by specifying "license_key_lookup_retry" parameter in the configuration file:
|
where:
- N - Number of retries looking for license key (or keys)
- T - Time between retries in seconds. If not specified 60 seconds is used
Example:
|
In this example, if the license key is not found during the initial scan, CHARON-AXP will scan 5 more times, waiting 60 seconds between them before it stops.
See General Settings section for more details.
© Stromasys, 1999-2024 - All the information is provided on the best effort basis, and might be changed anytime without notice. Information provided does not mean Stromasys commitment to any features described.